The metal-air battery is an active material that uses metals with negative electrode potential, such as magnesium, aluminum, zinc, mercury and iron, as the negative electrode, and oxygen or pure oxygen in the air as the positive electrode. Zinc-air battery is the most researched and widely used battery in the metal-air battery series. In the past 20 years, scientists have done a lot of research on secondary zinc-air battery. Sanyo Corporation of Japan has produced a large capacity secondary zinc-air battery. The zinc-air battery for tractor with a voltage of 125V and a capacity of 560A · h has been developed by using the method of air and electro-hydraulic force circulation. It is reported that it has been applied in vehicles, and its discharge current density can reach 80mA/cm2, and the maximum can reach 130mA/cm2. Some companies in France and Japan use the method of circulating zinc slurry to produce zinc-air secondary current, and the recovery of active substances is carried out outside the battery, with the actual specific energy of 115W · h/kg
Main advantages of metal-air battery:
1) Higher specific energy. Since the active material used in the air electrode is oxygen in the air, it is inexhaustible. In theory, the capacity of the positive electrode is infinite. In addition, the active material is outside the battery, so the theoretical specific energy of the air battery is much larger than that of the general metal oxide electrode. The theoretical specific energy of the metal air battery is generally more than 1000W · h/kg, which belongs to the high-energy chemical power supply.
(2) The price is cheap. The zinc-air battery does not use expensive precious metals as electrodes, and the battery materials are common materials, so the price is cheap.
(3) Stable performance. In particular, the zinc-air battery can work at a high current density after using powder porous zinc electrode and alkaline electrolyte. If pure oxygen is used to replace air, the discharge performance can also be greatly improved. According to theoretical calculation, the current density can be increased by about 20 times.
The metal-air battery has the following disadvantages:
1), the battery cannot be sealed, which is easy to cause the drying and rising of the electrolyte, affecting the capacity and life of the battery. If alkaline electrolyte is used, it is also easy to cause carbonation, increasing the internal resistance of the battery, and affecting the discharge.
2), the wet storage performance is poor, because the diffusion of air in the battery to the negative electrode will accelerate the self-discharge of the negative electrode.
3), the use of porous zinc as the negative electrode requires mercury homogenization. Mercury not only harms the health of workers but also pollutes the environment, and needs to be replaced by non-mercury corrosion inhibitor.
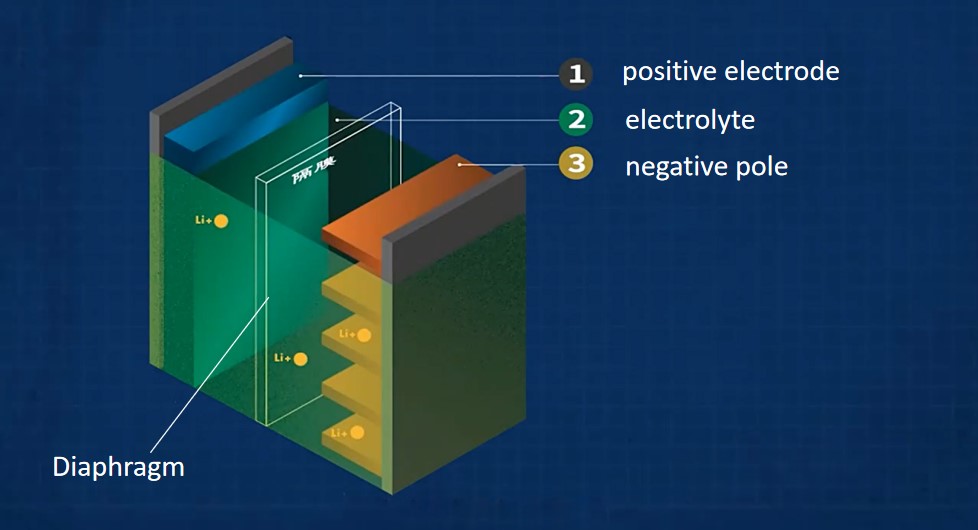
The metal-air battery is an active material that uses metals with negative electrode potential, such as magnesium, aluminum, zinc, mercury and iron, as the negative electrode, and oxygen or pure oxygen in the air as the positive electrode. Alkaline electrolyte aqueous solution is generally used as the electrolyte solution of metal-air battery. If lithium, sodium, calcium, etc. with more negative electrode potential are used as the negative electrode, because they can react with water, only non-aqueous organic electrolyte such as phenol-resistant solid electrolyte or inorganic electrolyte such as LiBF4 salt solution can be used。
Magnesium-air battery
Any pair of metal with negative electrode potential and air electrode can form corresponding metal-air battery. The electrode potential of magnesium is relatively negative and the electrochemical equivalent is relatively small. It can be used to pair with the air electrode to form a magnesium air battery. The electrochemical equivalent of magnesium is 0.454g/(A · h) Ф=- 2.69V。 The theoretical specific energy of magnesium-air battery is 3910W · h/kg, which is 3 times of that of zinc-air battery and 5~7 times of that of lithium battery. The negative pole of the magnesium-air battery is magnesium, the positive pole is oxygen in the air, the electrolyte is KOH solution, and the neutral electrolyte solution can also be used.
Large battery capacity, low cost potential and strong safety are the key advantages of magnesium ion batteries. The divalent characteristic of magnesium ion makes it possible to carry and store more electric charges, with a theoretical energy density of 1.5-2 times of lithium battery. At the same time, magnesium is easy to extract and widely distributed. China has an absolute resource endowment advantage. After making magnesium battery, its potential cost advantage and resource safety attribute are higher than lithium battery. In terms of safety, magnesium dendrite will not appear at the negative pole of the magnesium ion battery during the charging and discharging cycle, which can avoid the lithium dendrite growth in the lithium battery piercing the diaphragm and causing the battery to short circuit, fire and explosion. The above advantages make magnesium battery have great development prospects and potential。
With regard to the latest development of magnesium batteries, the Qingdao Institute of Energy of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has made good progress in magnesium secondary batteries. At present, it has broken through the technical bottleneck in the manufacturing process of magnesium secondary batteries, and has developed a single cell with an energy density of 560Wh/kg. An electric vehicle with a complete magnesium air battery developed in South Korea can successfully drive 800 kilometers, which is four times the average range of current lithium battery powered vehicles. A number of Japanese institutions, including Kogawa Battery, Nikon, Nissan Automobile, Tohoku University of Japan, Rixiang City, Miyagi Prefecture, and other industry-university-research institutions and government departments are actively promoting the large-capacity research of magnesium air battery. Zhang Ye, the research group of Modern Engineering College of Nanjing University, and others designed a double-layer gel electrolyte, which realized the protection of magnesium metal anode and the regulation of discharge products, and obtained a magnesium air battery with high energy density (2282 W h · kg-1, based on the quality of all air electrodes and magnesium negative electrodes), which is far higher than the magnesium air battery with the strategies of alloying anode and anti-corrosion electrolyte in the current literature.
In general, the magnesium battery is still in the preliminary exploration stage at present, and there is still a long way to go before large-scale promotion and application.
Post time: Feb-17-2023